Our research program is centered on the development of new catalytic transformations that unlock and harness the reactivity embedded in nitro-groups, anilines and azides to enable the synthesis of therapeutic N-heterocycles. Because N-heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive molecules, simplifying access to them is essential for the advancement of biological and medicinal studies. We have established aryl- and vinyl azides as useful nitrene precursors in metal-catalyzed N-atom transfer processes, and our discoveries of new reactivity patterns of metal N-aryl nitrenes have positioned us to establish them as a general phenomenon that is exhibited by nitroarenes, anilines and N-tosylhydrazones to streamline the synthesis of complex, functionalized molecules. The new methods for the construction of sp2- or sp3-C–NAr bonds, which emerged from these investigations, were used to create focused libraries of novel N-heterocycles, which were screened by UICentre for Drug Discovery’s HTS facility for potential leads and led to several translational projects that we have participated in. We have focused our efforts in drug discovery to examine the activity of our novel N-heterocycles to modulate the activity of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT), an important enzyme in the NAD salvage pathway, to identify potential small molecule therapeutics for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension, stroke and Alzheimer’s disease.
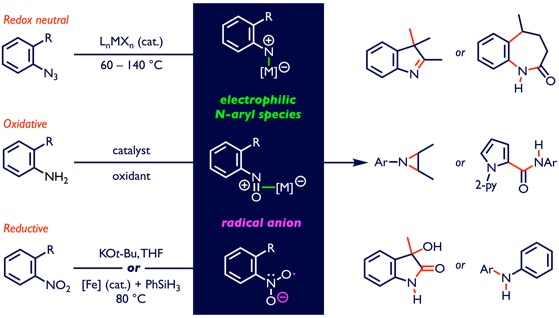
Accessing electrophilic N-aryl nitrogen species from azides, anilines, or nitroarenes.