|
 Cytochrome
P450 enzymes catalyze a number of oxidations in nature including
hydroxylation of hydrocarbons. The iron-oxo species, oxygen bound to
iron in the formal oxidation state of Fe(V), has long been thought to be the
electrophilic oxidant, but multiple reaction pathways appear to be
necessary to explain the results of mechanistic probe studies. Recent kinetic isotope effect studies in our lab
demonstrated that a second oxidizing species (presumed to be a
hydroperoxy-iron complex or iron-complexed hydrogen peroxide) effects
oxidations P450. Cytochrome
P450 enzymes catalyze a number of oxidations in nature including
hydroxylation of hydrocarbons. The iron-oxo species, oxygen bound to
iron in the formal oxidation state of Fe(V), has long been thought to be the
electrophilic oxidant, but multiple reaction pathways appear to be
necessary to explain the results of mechanistic probe studies. Recent kinetic isotope effect studies in our lab
demonstrated that a second oxidizing species (presumed to be a
hydroperoxy-iron complex or iron-complexed hydrogen peroxide) effects
oxidations P450.
Radical Cation
Clocks were recently developed for kinetic studies of enol ether
radical cations and the reaction that form these species. The work
involved using laser flash photolysis to make radicals that cleave
heterolytically to give radical cations. The radical cations then
cyclized to give distonic radical cations that have a strong chromophore
in the UV. Scheme 1 below shows one series of reactions. |
|
Coenzyme B-12-dependent
enzymes catalyze a number of radical conversions in nature. The
synthetic sequence in Scheme 2 below gives a radical precursor for laser
flash photolysis studies of the reaction catalyzed by methylmalonyl Co-A
mutase, a reversible radical isomerization of succinyl-CoA to
methylmalonyl-CoA. The SePh group in the precursor can be cleaved by
laser irradiation or in a radical chain reaction. The
diphenylcyclopropyl group is a “reporter” that will give a diphenylalkyl
radical that can be detected by UV as in the reaction in Scheme 1.
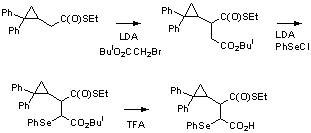
Scheme 2. Synthetic sequence for a radical
precursor for use in studies of the radical rearrangement catalyzed by
methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. |