 So
Pt is?
So
Pt is?
GASES
Know: 1L = 1000ml = 1000cm3 = 1 dm3
Know: 760mmHg = 1.00atm = 101.3kPa = 14.7psi
For Free: 1Pa = 1 Newton/m2 = F/A
Look! Laws... like the Law of the Burrito: "If a person ever eats a burrito with beans and hot sauce within five seconds, then he will produce enormous quantities of methane gas from the opposite end of his digestive system."
| Marek's Law | V a n n = # of moles |
| Charles Law | V a Tk |
| Boyle’s Law | V a 1/P |
So V
a
nTk
/P (what
does that a?
it reads, "V is proportional to nT/P")
V = RnTk
/P
or PV = nRTk
--
See p. 101 for R
values
Know eq.’s 4.12 & 4.13 p.104
--
Find density of O2 at 270C, 735 mmHg:
PV = nRT or PV = g/mm * RT
Also d = g/V =
P(MM)/RT
= (735/760atm)(32.0g/mol)
(0.0821L*atm/mol K)(300K)
= 1.26 g/L
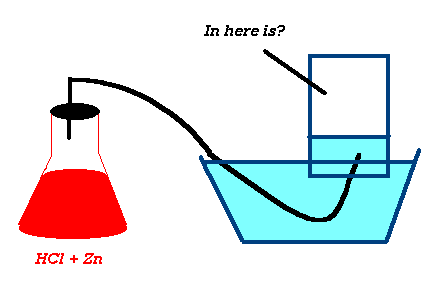
What mass of Zn is needed to react with hydrochloric acid to form 16.0L of H2(g) @ 200C, 735mmHg?
Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) --> ZnCl2(aq) +
H2(g)
Zn(s) + 2H+ (aq) --> Zn+2(aq)
+ H2(g)
V = 16.0L
T = 200C
P = 735mmHg
n = PV = (735/760atm)(16.0L) = 0.643 mol H2
RT (0.0821Latm/molK)(293K)
0.643 mol H2 x 1mol Zn x 65.38g Zn = 42.0g Zn
1 mol H2
1mol Zn
H2(g) + Cl2(g) --> 2HCl (g)
Coeff can stand for 1.____ 2. ____ 3.____.
p.108 and t-shirt
At STP, 22.4L/mol for ideal gas.
--
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure See p. 109
PT = S
Pi = P1
+ P2 +…+Pn
i=1
p. 111
P1 = X1PT
where X1 = n1/ntotal [mole fraction]
 So
Pt is?
So
Pt is?
How do you find PH2O? Appendix A1
Suppose we collect 256ml of gas at 220C, and a pressure of 752 mmHg. Find pressure of H2, moles H2, mole fraction H2.
Pt = PH2+ PH2O
--> PH2 = Pt – PH20
PH2 = 752 – 20 = 732mmHg
n=PV/RT= (732/760)(0.256)/(0.0821)/(295) = 0.0102 mol
XH2 = PH2/Pt = 732/752 = 0.973
Know p. 112
The postulates of the kinetic molecular theory can be stated as follows:
Gases consist of particles, which have the following properties:
KET = ½ mv2 =cTk
m = mass, v = speed, c = constant
See p.113
Diffusion vs. Effusion
(Rate Eff. A)/(Rate Eff. B)
= (Ave va)/(Ave vb)
= [(MMb)/(MMa)]½
= (time B)/(time A)
Ave v = (3RT/MM)½
For H2 at 00C,Know why gases deviate from ideal gases. See p. 119.
Low temperature, attractive force important.
High pressure, finite volume important.
Back to the Class Notes Homepage
|
|
|