|
|
P. 915 know #1, 2, and 3
Know 3 kinds of isomerism
P. 916
Alkanes (Hydrocarbons). Saturated: only with single bonds, has all the H (or other "stuff") it can hold.Fig 26.1
P. 918 ¬ Structural Isomers:
|
|
Margin P. 919
Table 26.1
|
Mary Eats Peaches, But Paul Has Had Only Nine Donuts. |
|
|
Nonane Decane |
|
See Rules P. 921 – name above 2 ![]()
Do HW 1 and 3
Unsaturated: double or triple-bonds on C, can hold more H’s.
| Alkenes: C=C | Alkynes: CºC |
|
(Page #949 7-d) |
1-ethyne (acetylene) |
Benzene: C6H6 – just know it.
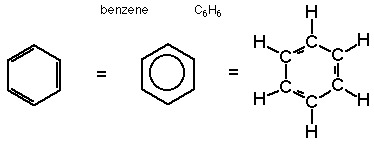
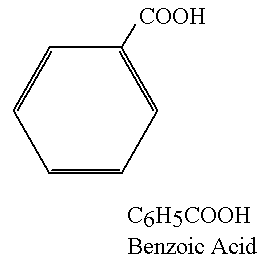
Benzoic Acid: C6H5COOH (H+ ions)
Skip p.926, Top 927, Exp3 skip
Don’t need to know any reaction except those I give you.
In H.W. 927® 937 You do not need to know all reactions- Just Functional Groups…see OH #3
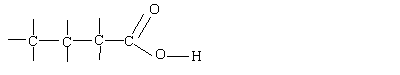
Explain: C3H7COOH, CH3COOH
You should be able to say ACID!
Butyric Acid
Butanoic Acid
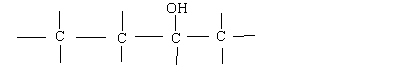
An Alcohol: 2-Butanol
Amines: Organic Bases
Read p.935
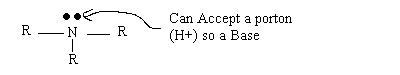
What if R=H?
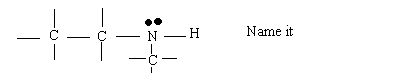
See Handout and p.937-Know it "Cold"
All 3 Types
 |
 |
Chiral Centers
Is this Optically Active?
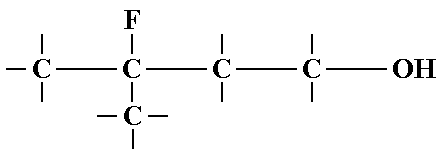
Where Centers?
2 Reactions
R3N: + H+ ® R3NH+
| + HC2H3O2 « [C2H3O2]– + | 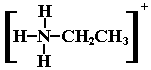 |
"A" Student Ester’s
Alcohol + Acid ® Ester + H2O
Name Above
1-Ethanol + Butanoic Acid ® Ethyl Butanoate + H20
HW 49 like this
![]()
There is other stuff in this chapter. But just know what I talked about.
Back to the Class Notes Homepage
 |
|