Early Greek
Philosophers
(and
their concepts of elements)
Thales—Water
(624-546 B.C.)
Anaximenes—Air
(560-500 B.C.)
Herakleitos—Fire
(536-470 B.C.)
Empedokles (490-439
B.C.)
Introduced
idea of Earth, Air, Fire, and Water.
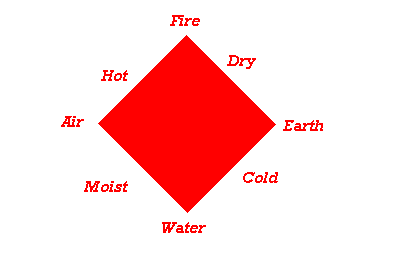
Tree = Fire, Water,
Earth
Dried Wood = Fire,
Earth
Ashes = Earth
Leucippus
(5th
century B.C.)
Democritus
(Born about 460 B.C.)
Plato
Aristotle
John Dalton
Generally credited
with being the first person to clearly and unequivocally state that all matter
was composed of atoms and to base this statement on what we would consider to be
a scientific pattern of reasoning.
Dalton’s Atomic
Postulates
p.34
- All elements are made of
atoms.
- Atoms can be neither
created or destroyed.
- Atoms of the same
element are the same.
- Atoms of different
elements are different.
- Compounds are made by
the union of atoms.
Laws
Upon Which Dalton’s Atomic Theory Was Based
Law of Conservation of
Mass See p. 34
Lavoisier –1774
Landolt – Late 1800’s
Law of Definite
Proportions See p. 34
Proust –1797
Law of Multiple
Proportions
If two elements form
more than one compound, then, for a given weight of the first element, the
weights of the second element that combine with the given weight of the first
will be in a ratio of small whole numbers.
Simple set of C-O
compounds that fit this.
Example
A
+ B
à
C
7.143g 6.972g
14.115g
A
+ B
à
D
3.265g 2.125g
5.390g
In
Compound C Wt. B/Wt. A =
6.972g/7.143g = 0.9761g B/g A
In
Compound D Wt. B/Wt. A =
2.125g/3.265g
=0.6508g B/g A
0.9761/0.6508 = 1.50 =
3/2
New
Problem Follows
#1
#2
Given:
%P =
22.54
= 14.88
%Cl =
77.46
= 85.12
Find: (a) mass in g of Cl to
1 g P
(b) also the 2 formulas
(a) Hint: Pick 100.0 g
basis so you have
#1
22.54 g P
#2 14.88 g P
77.46 g
Cl
85.12 g Cl
Cl
= 77.46 g = 3.437 Cl
= 85.12 g = 5.720
P
22.54
g
P 14.88 g
(b) #2 5.720 =
1.664 or 1 2/3 or 5 Cl in 2
#1
3.473
3 Cl in 1
To get formulas: #1 (2 done
same!)
22.54 g P C
(1 mol P/30.97 g P) = 0.7278 mol P
77.46 g Cl C
(1 mol Cl/35.45 g Cl) = 2.185 mol Cl
2.185 mol Cl
= 3.002 Cl or PCl3 (PCl5)
0.7278 mol
P
P
Stoney’s
Interpretation of Faraday’s Experiments
- Electricity is
particulate.
- The atom is electrical
in nature.
- Whatever is electrical
in the atom is also particulate.
Coined the word
"electron" for this particle in 1891.
Thomson’s
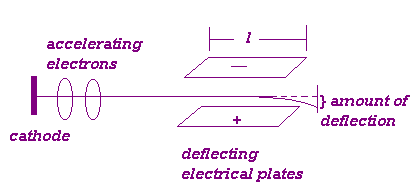
Determination of e/m Method 2 Passed cathode rays
through a region where they could be deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
 Click
here to see a cathode ray video!!!
Particles were
subjected to an electrical force as they passed between the deflecting plates.
Click
here to see a cathode ray video!!!
Particles were
subjected to an electrical force as they passed between the deflecting plates.
F = eF = ma
d
= ½ at2
a = eF/m
d
= ½ (eF/m)(l/n)2
e/m = 2
d n 2 /Fl
2
But we don’t know n!!!!!!
Thomson
then balanced the electrical field with an opposing magnetic field, so the
electron passed through undeflected. Since the electrical and magnetic forces
must now be balanced,
Hen
= eF n
= F/H
And e/m = Zdn2
/Fl2 = ZdF2
/Fl2 H2 = ZdF
/H2l2 J.J.Thomson
– 1898 Determine the charge
to mass ratio. E/m for electrons. ALL ELECTRONS ARE THE SAME!!!!!!!!!!
The positive parts of
different atoms are different. Presents one of the
second "models" of the atom, the plum-pudding model.
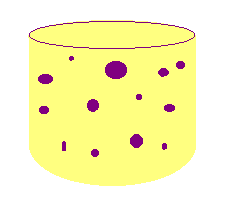 Millikan’s Oil
Drop Experiment 1909
Millikan’s Oil
Drop Experiment 1909
First Nobel Prize winner in the US!!
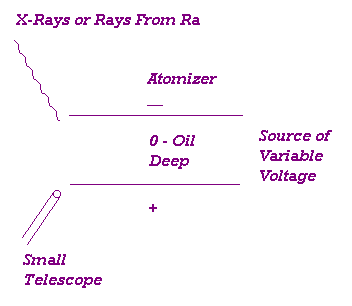
APPARATUS
Click
here to see an animation of Gold Foil!!!
If you want a 6.0M solution
of HCl and you need 200 mL, how much 12.0M HCl do you need?
Dilution: What is true?
Moles HCl before =
Moles HCl after MBxVB
= MAxVA
VB = MAxVA
= 6.0M x 200ml
MB
12.0M VB = 100ml
of Concentrated HCl
You have 2.5M NaCl solution
in 250 ml. You add 75 ml of water. What is [NaCl] = ? "the concentration
of"
If I have a 1M solution
& I pour ½ out, what is the [ ] of the remaining solution?
Back to the Class Notes Homepage





