CHAPTER 13
An Easy Chap- Just Read!
A basic goal of Chemistry is to predict the extent to which a reaction can be expected to occur.
K’s allow us to make such predictions…
See OH #2 "The Classic"
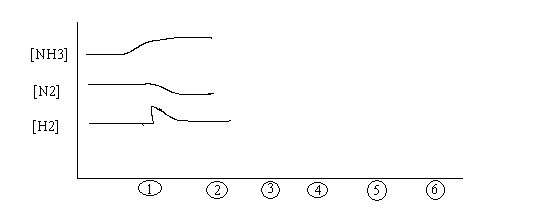
See Fig 13.2- How do we know when we have reaction equilibrium?
Kc = [NO2]2
means]"The concentration of…"[N2O4]
[
This is a constant provided what is true?
*Know Equ 13.2 by heart on p.434
Another classic esp. #13.1
(How would you know you reached equilibrium here?)
Know Coefficient Rule
Reciprocal Rule
Multiple Equilibrium Rule
When you combine (i.e. add) individual equations you Multiply their K’s to obtain an Equ. Constant for the Net Reaction.
K(net) = K1 x K2
Gaseous Phosphorus PentaChloride* Decomposes to Gaseous Phosphorus Trichloride and Chlorine. Suppose
2.00 mole of Phosphorus Pentachloride in a 2.00 L Vessel comes to Equilibrium. What are the Equilibrium Concentrations?
Kc= 1.0 x 10-3
See p. 447
N2 + 3H2« 2NH3 + 92.2kJ

Read Well p.451
********************************************
Kp = Kc x (RT) D n(g)
T is the absolute temp
D n(g) ® change in moles of gas
For the above Kc = 9.5
R = 0.0821 at 300° C, What is Kp =?.
****************************************
Fritz Haber invented synthesis of ammonia from it’s elements.
Kc = .50 @ 400° C
Find D H in kJ
*********************************************
The relation between Kc and temp is given by the VanHoff equation.
ln K2 =
D H x T2 – T1Analogous to Clausius Clapeyron
Change in H = Enthalpy change for the forward reaction in "J"
T2, T1 Are absolute temps
K2, K1 are equilibrium constants at T2, T1
R = 8.31 J/mole K gas law constant
Use to calculate K at one temp when you know change in H and K at another Temp.
Problem: For the system 2HI Û H2 + I2 if Kc = 0.016 at 520 C and change in H = +10.4 kJ find Kc at 600 C
****************New Problem***************
Fritz Haber invented synthesis of ammonia from it’s elements. 1) Write the Equation. 2) Write the expression for the equation constant.
3) Given Kc = 650 @ 200 C
Kc = 0.50 @ 400 C
4) Given above and your solution to #3 find Kc at 600 C
BECOME FRIENDS WITH YOUR CALCULATOR!!!
******************************
Name Period________
You have the Following World Famous A and B. They React as Follows:
A(g) + 2B(g)« AB2(g)
If the Initial Concentrations are
[A]o= 0.100M; [B]o= 0.200M; [AB2]o = 0.050M,
At Equilibrium Little Becky Chemist Finds [AB2] to be 0.025M.
What is [A]; [B] Equilibrium Concentrations?
What is Kc?
Back to the Class Notes Homepage
 |
|